- Home /
Shader to dilate a binary image
I am trying to write a shader to achieve dilation in a binary image.
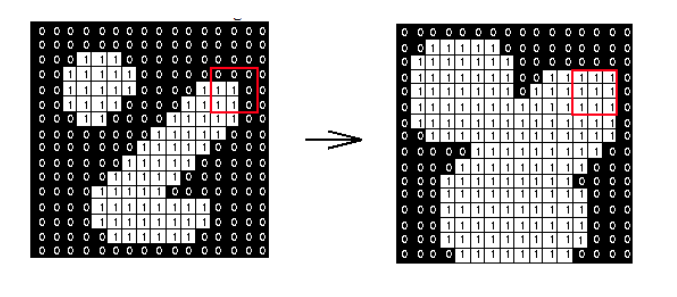
If the pixel in the center of 3X3 is 1, make surrounding pixels 1
Pseudo Code: Step through all pixels around the current target pixel. Once a pixel is found that is 1 break the loops and set the target pixel to 1. This way the target pixel will become 1 if at least one pixel around it is 1.
Any help in coding this is appreciated.
Answer by poisoned_banana · Apr 18, 2018 at 01:40 PM
I wrote a simple shader. It offsets the texture in 8 directions and creates a final color of all these pixel. So if one of these pixel happens to white, the final pixel is also becoming white.
RESULT 
CODE
Shader "Unlit/Dilation"
{
Properties
{
_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {} // main texture of this shader
_PixelOffset("Distance",Range(0,1)) = 1 // use: 1 / textureDimension (16x16 => 1/16 = 0.0625)
}
SubShader
{
Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" }
LOD 100
Pass
{
CGPROGRAM
#pragma vertex vert
#pragma fragment frag
#include "UnityCG.cginc"
struct appdata
{
float4 vertex : POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
};
struct v2f
{
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float4 vertex : SV_POSITION;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTex_ST;
float _PixelOffset;
v2f vert (appdata v)
{
v2f o;
o.vertex = UnityObjectToClipPos(v.vertex);
o.uv = TRANSFORM_TEX(v.uv, _MainTex);
return o;
}
fixed4 frag (v2f i) : SV_Target
{
//min and max Vector
float2 _min = float2(0,0);
float2 _max = float2(1,1);
//get the color of 8 neighbour pixel
fixed4 U = tex2D(_MainTex,clamp(i.uv + float2(0,_PixelOffset),_min,_max));
fixed4 UR = tex2D(_MainTex,clamp(i.uv + float2(_PixelOffset,_PixelOffset),_min,_max));
fixed4 R = tex2D(_MainTex,clamp(i.uv + float2(_PixelOffset,0),_min,_max));
fixed4 DR = tex2D(_MainTex,clamp(i.uv + float2(_PixelOffset,-_PixelOffset),_min,_max));
fixed4 D = tex2D(_MainTex,clamp(i.uv + float2(0,-_PixelOffset),_min,_max));
fixed4 DL = tex2D(_MainTex,clamp(i.uv + float2(-_PixelOffset,-_PixelOffset),_min,_max));
fixed4 L = tex2D(_MainTex,clamp(i.uv + float2(-_PixelOffset,0),_min,_max));
fixed4 UL = tex2D(_MainTex,clamp(i.uv + float2(-_PixelOffset,_PixelOffset),_min,_max));
//add all colors up to one final color
fixed4 finalColor = U + UR + R + DR + D + DL + L + UL;
//return final color
return finalColor;
}
ENDCG
}
}
}
Answer by jbedo · Feb 14, 2019 at 12:26 AM
It is possible to do the same with a grayscale image? I mean what to change if the pixel value is higher than black?.
Your answer